1. Classification of Polymers & Polymerization Process: Addition (chain reaction) and condensation (step reaction) polymerizations
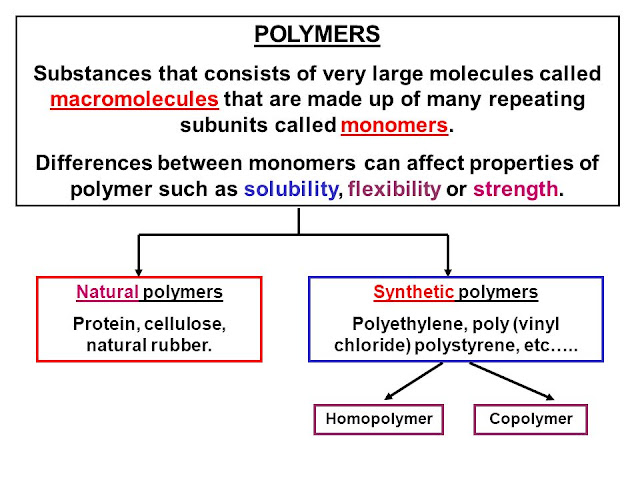
2. Fundamental concept of the Following Polymer:
Homopolymers and heteropolymers. low density and high density polymers and
their properties. Copolymers, alternating, random, block and graft copolymers.
elastomer, thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers and their properties. fiber
and elastomer.
3. Mechanism
of polymerization: Redical, cationic and anionic polymerization, and their
kinetics, chain termination, chain transfer, chain retardation and chain
inhibition.
4. Co-ordination
polymerization: Fluid-bed process, Ziegler-Natta catalysis, mechanism of
co-ordination polymerization and its kinetics, metal oxide catalyzed and olefin
polymerizations. ring opening polymerization.
5. Configuration
of polymers: Syndiotactic, isotactic, atactic polymers.
6.
Some
important polymers: Production of monomer unit, physical properties and
important uses of polythene, polyvinylchloride (PVC), polystyrene,
polybutylene, polybuatadiene-styrene, neoprene, polymethylmethacrylate,
polyacrylonitrile, polyvinylacetate, polyamides: Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Nylon 11
and Nylon 12, silk and wool.

Post a Comment